
Introduction
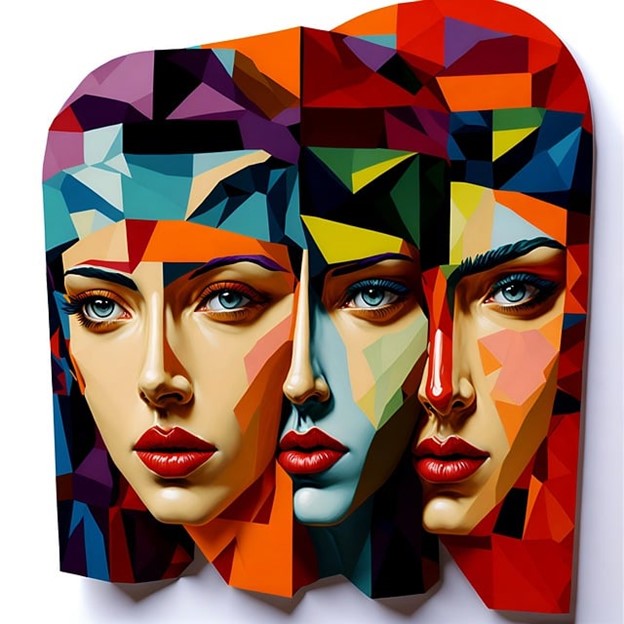
Cubism, pioneered by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque in the early 20th century, revolutionized the art world with its fragmented, geometric forms. Fast forward to the digital age, where artists are reimagining this movement through a modern lens, leveraging technology to create captivating digital Cubist artworks. In the realm of digital art, the spirit of Cubism, an art movement that revolutionized the way we perceive and represent reality, finds a new lease on life. I, Aquinnah Marcus, will take a stroll down the lane of digital Cubism, empowering aspiring artists to embrace the fragmented and multifaceted nature of the digital world and create captivating digital masterpieces.

Understanding Cubism
Digital Cubism echoes the core principles of traditional Cubism, emphasizing the fragmentation of forms, the interplay of multiple perspectives, and the exploration of dimensionality within a two-dimensional plane. However, in the digital realm, artists have the freedom to manipulate and transform these elements to create new and innovative expressions.
Origins and Principles
Cubism challenged traditional representation by deconstructing subjects into geometric shapes, emphasizing multiple perspectives within a single frame. It aimed to depict the essence of the subject rather than its literal representation.
Characteristics
Cubist artworks are characterized by fractured forms, geometric shapes, and a sense of disassembled reality. Artists employed techniques like fragmentation, abstraction, and simultaneous viewpoints to convey depth and movement.
Digital Cubism: A Contemporary Evolution

Utilizing Digital Tools
Modern artists leverage digital tools such as graphic software (like Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or even specialized 3D modeling software) and tablets to explore Cubism in the digital realm.
Layering and Manipulation
Digital platforms allow for intricate layering and manipulation of shapes and forms. Artists create layers akin to facets, constructing compositions by rearranging and distorting elements, capturing the essence of Cubism’s fragmented reality.
Techniques in Digital Cubism

Geometric Abstraction
Digital Cubist artists emphasize geometric shapes, utilizing squares, triangles, and polygons to deconstruct subjects. They experiment with layers and opacity, juxtaposing shapes to recreate fragmented perspectives.
Multiple Viewpoints
Exploring multiple viewpoints within a single composition remains a hallmark of Cubism. Digital artists simulate various perspectives, overlaying and intertwining elements to convey depth and dynamism.
Color and Texture Experimentation
Color plays a pivotal role in digital Cubism. Artists experiment with vibrant palettes, contrasting hues, and textures to add depth and visual interest, intensifying the fractured nature of the artwork.
Fragmentation and Reassembly
Digital Cubism embraces the fragmentation of forms, breaking down objects and scenes into their constituent parts and reassembling them in unexpected ways. This process challenges traditional notions of representation and allows artists to explore the multifaceted nature of reality in the digital age.
Multiple Perspectives
Digital Cubism utilizes multiple perspectives, showcasing an object or scene from various angles simultaneously. This technique creates a dynamic and multifaceted representation, revealing hidden dimensions and challenging viewers to perceive reality from multiple viewpoints.
Dimensionality in Two Dimensions
Digital Cubism explores the illusion of depth and dimensionality within the confines of a two-dimensional plane. Artists utilize techniques such as perspective, color, and shading to create a sense of depth and volume, blurring the lines between two-dimensional and three-dimensional representation.
Digital Tools
Digital tools provide artists with unprecedented flexibility and control in their pursuit of digital Cubism. Software such as Adobe Photoshop and Blender allows artists to manipulate shapes, apply textures, and experiment with lighting effects, expanding the creative possibilities of this art form.
Embracing 3D Elements
Incorporating Three-Dimensional Aspects:
Advancements in technology allow artists to incorporate 3D elements into digital Cubist works. By integrating 3D models or elements, artists infuse depth and a sense of tangibility into their compositions.
Interactive and Dynamic Art:
Some artists take digital Cubism a step further by creating interactive or dynamic artworks. These pieces might utilize animation, interactivity, or even augmented reality to engage viewers and bring Cubism to life in new ways.
The Impact of Digital Cubism
Evolving Artistic Boundaries
Digital Cubism pushes the boundaries of traditional Cubism, offering artists a versatile platform to experiment and innovate. It invites a new generation of artists to explore this iconic movement in a contemporary context.
Accessibility and Outreach
Digital platforms enable wider accessibility and outreach for digital Cubist artworks. Social media, online galleries, and digital exhibitions provide avenues for artists like Marcus to showcase their creations to a global audience.
Conclusion
Digital Cubism stands as a testament to the enduring influence of an iconic art movement reimagined through modern technology, it is the evolution of art, paving the way for a dynamic future where Cubism remains a vibrant and relevant artistic force.













Got a Questions?
Find us on Socials or Contact us and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.